Discriminative Color Descriptors
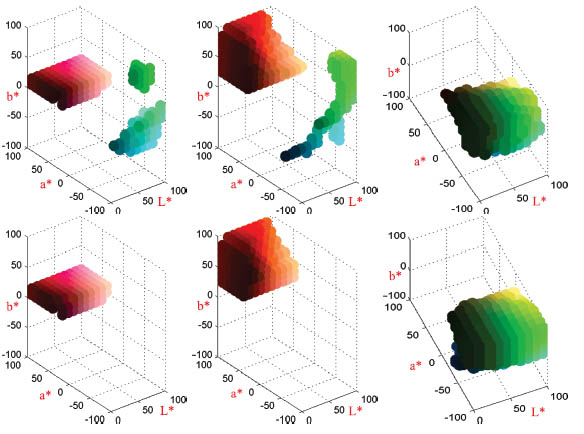
In this work we have taken an information theoretic approach to color
description. We cluster color values together based on their discriminative
power in a classification problem. The clustering has the explicit objective
to minimize the drop of mutual information of the final representation.
We show that such a color description automatically learns a certain degree
of photometric invariance. We also show that a universal color representation,
which is based on other data sets than the one at hand, can obtain competing
performance. Experiments show that the proposed descriptor outperforms
existing photometric invariants. Furthermore, we show that combined with
shape description these color descriptors obtain excellent results on
four challenging datasets, namely, PASCAL VOC 2007, Flowers-102, Stanford
dogs-120 and Birds-200.
Rahat Khan, Joost van de Weijer, Fahad Khan, Damien Muselet, Christophe Ducottet, Cecile Barat, Discriminative Color Descriptors, Proc. (CVPR)
-
Learning Color Names for Real-World Applications.
IEEE Transaction in Image Processing (TIP), vol 18 (7):1512-1524, July 2009.
-
,
Coloring Local Feature Extraction.
Proc. ECCV, Part II, 334-348, Graz, Austria, 2006.
-
,
Parametric fuzzy sets for automatic color naming.
Journal of the Optical Society of America A, vol.25(10), 2008.
We release the code of descriminative color descriptors in a C-implementation and a MATLAB implementation. The code can be downloaded here.
In addition the code includes implementations of the color descriptors described in earlier papers: